Postgres Backup
Backup
-
Navigate to the backup directory to check the file:
cd /backup ls -a -
Then create the backup.sql file and grant permissions:
chmod 777 backup.sql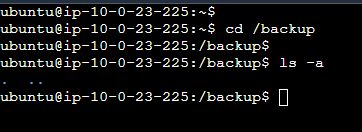
Configure PostgreSQL to perform backups to the /backup directory using tools like pg_dump.
This guide explains how to use the pg_dump command to create a backup of a PostgreSQL database. The specific command provided is used to export data from a PostgreSQL database named test_erp into a file called backup.sql. Prerequisites:
-
Ensure you have administrative access to the PostgreSQL server.
-
Confirm that the PostgreSQL service is operational.
-
Have sufficient permissions to access and edit the test_erp database.
-
Ensure there is enough disk space in the /backup directory for the backup file. The command is as follows:
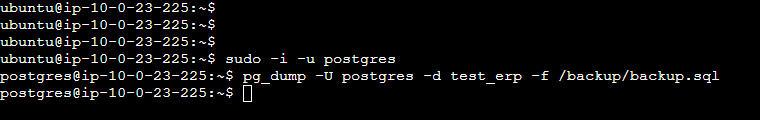
sudo -i -u postgres pg_dump -U postgres -d test_erp -f /backup/backup.sqlsudo -i -u postgres:sudo: Execute a command as another user, usually with elevated rights.-i: Simulate initial login as the user (in this case, postgres).-u postgres: Specify that this command is executed under the postgres user account, typically the administrative user of the PostgreSQL server.
pg_dump: This command is used to export a PostgreSQL database into a file.- Options:
-U postgres: Specify the username to connect to the database. Here, it is the postgres user.-d test_erp: Select the database to export. In this case, the database is test_erp.-f /backup/backup.sql: Specify the file where the backup will be written. Here, it is /backup/backup.sql.
-
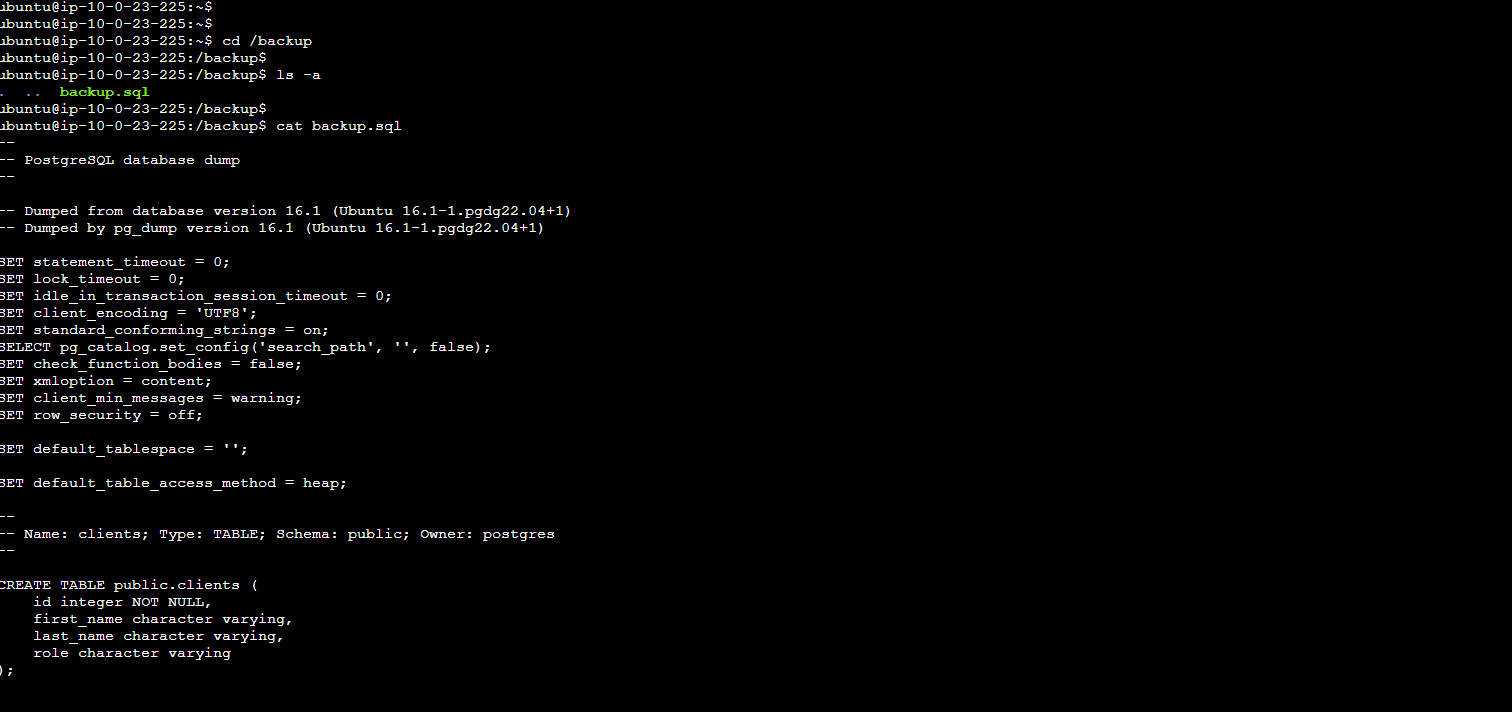
Perform a check of the backup.sql file:
cd /backup ls -a cat backup.sql